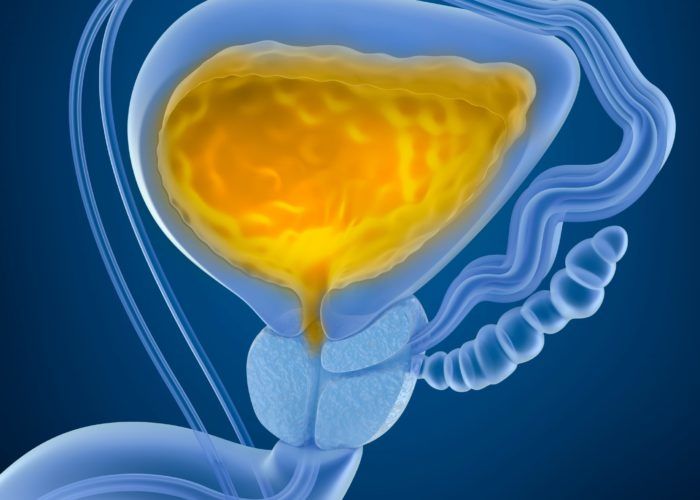
Urinary retention is a situation where your bladder is not releasing all of your urine. Urine that’s retained can back up in your system and potentially lead to a lot of complications.
Complications of urinary retention
These complications can include:
- Edema
- A loss of protein in your urine
- A build-up of ammonia (strong ammonia-smelling urine)
- Sugar in your urine
- Loss of muscle
- Fatigue
- Itchiness
- Brain fog
Diabetes is a big cause of urinary retention. High levels of sugar damage the capillaries of the kidneys and can lead to permanent damage. On top of that, a person with diabetes typically consumes a high-carb diet, which can cause fluid retention.
Common causes of urinary retention
Common causes of urinary retention:
- Diabetes
- A high-carb diet
- Age
- An enlarged prostate
- Fibroids
- Excess sodium consumption with low potassium consumption
- A problem with the autonomic nervous system
- Pregnancy
- Kidney stones
- Bladder stones
- Certain medications
What to do?
What to do for urinary retention:
- Cut out carbs and sugar
- Increase your fluids (3 liters in the first part of the day)
- Consume herbal diuretic alternatives (dandelion greens and watercress)
- Consume more potassium foods or an electrolyte powder (at least seven cups of vegetables per day)
- Consume a moderate amount of protein (3-6 oz per meal)







My husband wasn’t able to urinate all of a sudden and had to be catheterized for several weeks (which he hated). At first it was thought that he had an enlarged prostate (he’s 75). Then a colonoscopy found that he had severe diverticulosis, and his constipated colon was pushing on his prostate which in turn was closing off his urethra. Now he is on Metamusil for constipation which has helped tremendously. We basically had to figure out the constipation part ourselves as the urologist was clueless about anything not part of the urinary system and prostate.
I’m dealing with edema and enlarged bladder as I type this. I had a catheter put in. Next Wednesday I see Urologist and hopefully have catheter removed but, I’m rather fearful of it hurting. It hurt like hell when it was put in!!